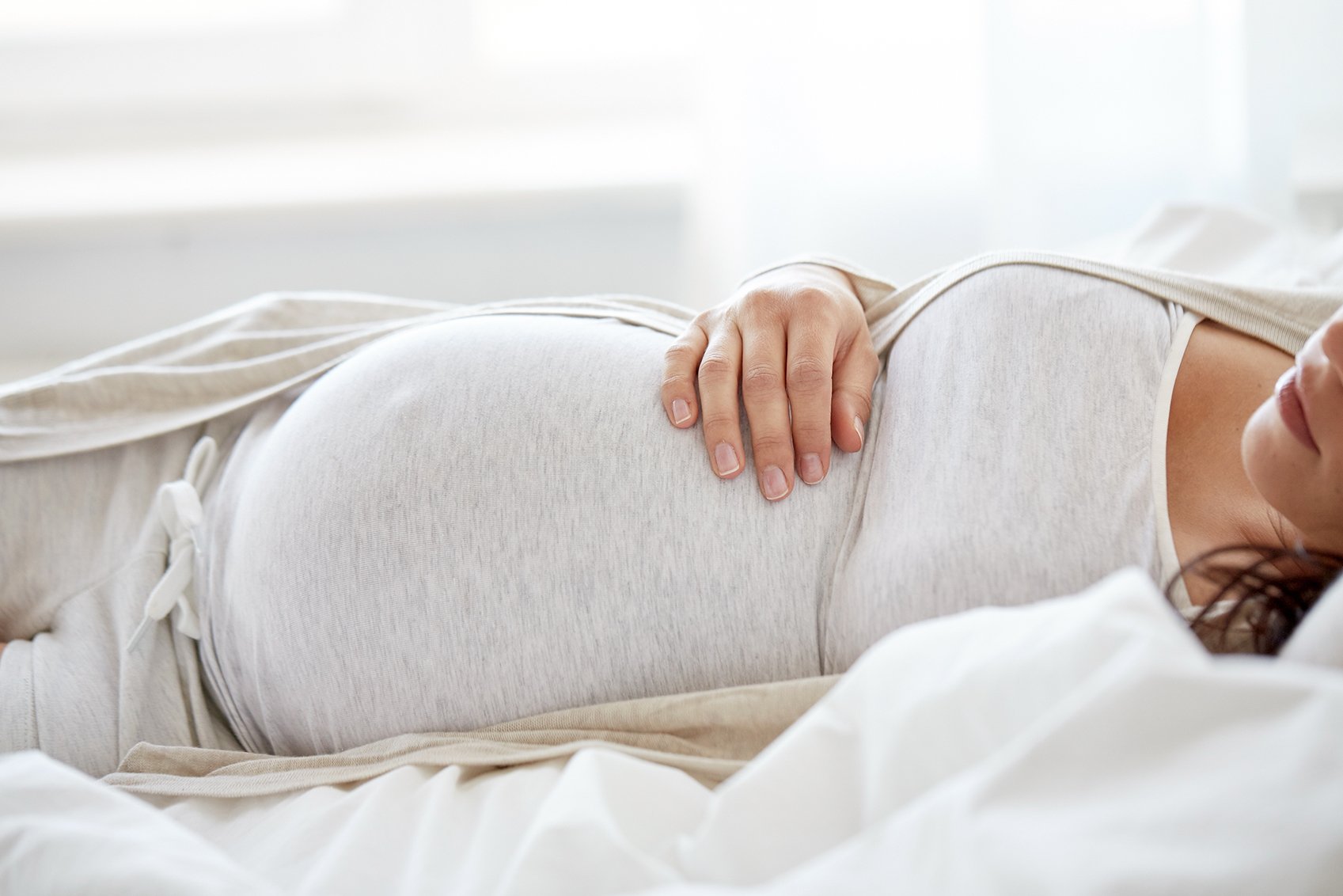
Optimal Sleep Positions and Solutions During Pregnancy
The best sleep position during pregnancy is on your left side with your knees bent and a pillow between your legs. Sleeping on your left side prevents the liver from applying pressure on the uterus and improves blood circulation to the uterus and the fetus. Increased blood circulation can help alleviate low back pain. Sleeping on the left side can improve the body’s lymphatic system (located predominantly on the left side of the body) which carries infection fighting white blood cells throughout your body and helps with detoxification.1
Some common sleep problems that occur during pregnancy include the following:
Insomnia
Physical discomfort and stress are common causes of insomnia during pregnancy. Avoid drug therapy as this can harm a developing fetus. Meditation and herbal tea can help relax both the muscles and the mind. Also, turn off all electronic communications devices one hour prior to bedtime to calm the mind. Regularly scheduled acupuncture treatments can help with overall pain and stress relief.
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
RLS can appear as a twitching or tingling of the legs that occurs in the evening or during the night which can disturb sleep. Stretching the legs can temporarily relieve these symptoms. Prenatal vitamins that include folate and iron supplements can help reduce these symptoms. Gently massaging your legs just prior to bed time can also help alleviate RLS.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder in which breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep. If you are experiencing sleep apnea, schedule a consultation with your doctor.
Nocturnal Gastroesophageal Reflux (nighttime GERD or heartburn)
GERD is a common experience during pregnancy. Avoid spicy and acidic foods to help minimize nocturnal GERD. “Grazing” or eating small meals frequently during the day rather than eating three large meals can help cut down on GERD. Consult with your doctor regarding any over the counter antacids.2
Frequent Nighttime Urination
As the fetus grows larger, it puts pressure on the urinary bladder. This is a common in all pregnancies. Drink water continuously during the daytime hours, then cut back 1 or 2 hours prior to bedtime. Keep in mind that this is a temporary inconvenience.3